Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Kuroki, Ryota; Blaber, M.
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.953 - 957, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)Symfoil-4P is a 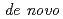 protein exhibiting the threefold symmetrical beta-trefoil fold designed based on the human acidic fibroblast growth factor. First three asparagine-glycine sequences of Symfoil-4P are replaced with glutamine-glycine (Symfoil-QG) or serine-glycine (Symfoil-SG) sequences protecting from deamidation, and His-Symfoil-II was prepared by introducing a protease digestion site into Symfoil-QG so that Symfoil-II has three complete repeats after removal of the N-terminal histidine tag. The Symfoil-QG and SG and His-Symfoil-II proteins were expressed in
protein exhibiting the threefold symmetrical beta-trefoil fold designed based on the human acidic fibroblast growth factor. First three asparagine-glycine sequences of Symfoil-4P are replaced with glutamine-glycine (Symfoil-QG) or serine-glycine (Symfoil-SG) sequences protecting from deamidation, and His-Symfoil-II was prepared by introducing a protease digestion site into Symfoil-QG so that Symfoil-II has three complete repeats after removal of the N-terminal histidine tag. The Symfoil-QG and SG and His-Symfoil-II proteins were expressed in 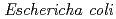 as soluble protein, and purified by nickel affinity chromatography. Symfoil-II was further purified by anion-exchange chromatography after removing the HisTag by proteolysis. Symfoil-QG and II crystals gave 1.5 and 1.1
as soluble protein, and purified by nickel affinity chromatography. Symfoil-II was further purified by anion-exchange chromatography after removing the HisTag by proteolysis. Symfoil-QG and II crystals gave 1.5 and 1.1 , resolution, respectively. The refined crystal structure of Symfoil-II showed pseudo-threefold symmetry as expected from other Symfoils.
, resolution, respectively. The refined crystal structure of Symfoil-II showed pseudo-threefold symmetry as expected from other Symfoils.
 -glucanase from
-glucanase from 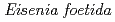
Arimori, Takao*; Ito, Akihiro*; Nakazawa, Masami*; Ueda, Mitsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.884 - 889, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:65.37(Instruments & Instrumentation)The saccharification process is essential for bioethanol production from woody biomass including celluloses. Cold-adapted cellulase, which has sufficient activity at low temperature ( 293 K), is capable of reducing heating costs during the saccharification process and is suitable for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Endo-1,4-
293 K), is capable of reducing heating costs during the saccharification process and is suitable for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Endo-1,4- -glucanase from the earthworm Eisenia fetida (EF-EG2) belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 9 has been shown to have the highest activity at 313 K, and also retained a comparatively high activity at 283 K. The recombinant EF-EG2 was purified expressed in Pichia pastoris, and then grew needle-shaped crystals with dimensions of 0.02
-glucanase from the earthworm Eisenia fetida (EF-EG2) belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 9 has been shown to have the highest activity at 313 K, and also retained a comparatively high activity at 283 K. The recombinant EF-EG2 was purified expressed in Pichia pastoris, and then grew needle-shaped crystals with dimensions of 0.02  0.02
0.02  1 mm. The crystals belonged to the space group P3221 with unit-cell parameters of
1 mm. The crystals belonged to the space group P3221 with unit-cell parameters of  =
=  =136
=136  ,
,  = 55.0
= 55.0  ,. The final model of EF-EG2, including 435 residues, two ions, seven crystallization reagents and 696 waters, was refined to a crystallographic
,. The final model of EF-EG2, including 435 residues, two ions, seven crystallization reagents and 696 waters, was refined to a crystallographic  -factor of 14.7% (free
-factor of 14.7% (free  -factor of 16.8%) to 1.5
-factor of 16.8%) to 1.5  , resolution. The overall structure of EF-EG2 has an (
, resolution. The overall structure of EF-EG2 has an ( /
/ )
) barrel fold which contains a putative active-site cleft and a negatively charged surface. This structural information helps us understand the catalytic and cold adaptation mechanisms of EF-EG2.
barrel fold which contains a putative active-site cleft and a negatively charged surface. This structural information helps us understand the catalytic and cold adaptation mechanisms of EF-EG2.
 -glucosyltransferase from
-glucosyltransferase from 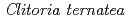
Hiromoto, Takeshi; Honjo, Eijiro*; Tamada, Taro; Noda, Hisanobu*; Kazuma, Kohei*; Suzuki, Masahiko*; Kuroki, Ryota
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.894 - 898, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:86.45(Instruments & Instrumentation)Flowers of the butterfly pea ( ) accumulate a group of polyacylated anthocyanins, named ternatins, in their petals. The first step in ternatin biosynthesis is the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin, a reaction catalyzed in
) accumulate a group of polyacylated anthocyanins, named ternatins, in their petals. The first step in ternatin biosynthesis is the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin, a reaction catalyzed in  by UDP-glucose:anthocyanidin 3-
by UDP-glucose:anthocyanidin 3- -glucosyltransferase (
-glucosyltransferase ( 3GT-A; AB185904). To elucidate the structure-function relationship of
3GT-A; AB185904). To elucidate the structure-function relationship of  3GT-A, recombinant
3GT-A, recombinant  3GT-A was expressed in
3GT-A was expressed in  and its tertiary structure was determined to 1.85
and its tertiary structure was determined to 1.85  , resolution by using X-ray crystallography. The structure of
, resolution by using X-ray crystallography. The structure of  3GT-A shows a common folding topology, the GT-B fold, comprised of two Rossmann-like
3GT-A shows a common folding topology, the GT-B fold, comprised of two Rossmann-like  /
/ /
/ domains and a cleft located between the N- and C-domains containing two cavities that are used as binding sites for the donor (UDP-Glc) and acceptor substrates. By comparing the structure of
domains and a cleft located between the N- and C-domains containing two cavities that are used as binding sites for the donor (UDP-Glc) and acceptor substrates. By comparing the structure of  3GT-A with that of the flavonoid glycosyltransferase
3GT-A with that of the flavonoid glycosyltransferase 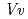 GT1 from red grape (
GT1 from red grape ( ) in complex with UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose and kaempferol, locations of the catalytic His-Asp dyad and the residues involved in recognizing UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose were essentially identical in
) in complex with UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose and kaempferol, locations of the catalytic His-Asp dyad and the residues involved in recognizing UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose were essentially identical in  3GT-A, but certain residues of
3GT-A, but certain residues of 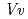 GT1 involved in binding kaempferol were found to be substituted in
GT1 involved in binding kaempferol were found to be substituted in  3GT-A. These findings are important for understanding the differentiation of acceptor-substrate recognition in these two enzymes.
3GT-A. These findings are important for understanding the differentiation of acceptor-substrate recognition in these two enzymes.
Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Yamada, Taro*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Ohara, Takashi; Katagiri, Masaki*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.994 - 998, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:85.87(Instruments & Instrumentation)The IBARAKI biological crystal diffractometer, iBIX, is a high-performance time-of-flight neutron single-crystal diffractometer for elucidating mainly the hydrogen, protonation and hydration structures of biological macromolecules in various life processes. Since the end of 2008, iBIX has been available to user's experiments supported by Ibaraki University. Since August 2012, an upgrade of the 14-existing detectors has begun and 16 new detectors have been installed for iBIX. The total measurement efficiency of the present diffractometer has been impoved by one order of magnitude from the previous one with the increasing of accelerator power. In December 2012, commissioning of the new detectors was successful, and collection of the diffraction dataset of ribonucrease A as a standard protein was attempted in order to estimate the performance of the upgraded iBIX in comparison with previous results. The resolution of diffraction data, equivalence among intensities of symmetry-related reflections and reliability of the refined structure have been improved dramatically. iBIX is expected to be one of the highest-performance neutron single-crystal diffractometers for biological macromolecules in the world.
Yokoyama, Takeshi*; Mizuguchi, Mineyuki*; Nabeshima, Yuko*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Yamada, Taro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.834 - 837, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:33.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)Transthyretin (TTR) is a tetrameric protein. TTR misfolding and aggregation are associated with human amyloid diseases. Dissociation of the TTR tetramer is believed to be the rate-limiting step in the amyloid fibril formation cascade. Low pH is known to promote dissociation into monomer and the formation of amyloid fibrils. In order to reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying pH sensitivity and structural stabilities of TTR, neutron diffraction studies were conducted using the IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer with the time-of-flight method. Crystals for the neutron diffraction experiments were grown up to 2.5 mm for four months. The neutron crystal structure solved at 2.0
for four months. The neutron crystal structure solved at 2.0  revealed the protonation states of His88 and the detailed hydrogen-bond network depending on the protonation states of His88. This hydrogen-bond network is involved in monomer-monomer and dimer-dimer interactions, suggesting that the double protonation of His88 by acidification breaks the hydrogen-bond network and causes the destabilization of the TTR tetramer. Structural comparison with the X-ray crystal structure at acidic pH identified the three amino acid residues responsible for the pH sensitivity of TTR. Our neutron model provides insights into the molecular stability related to amyloidosis.
revealed the protonation states of His88 and the detailed hydrogen-bond network depending on the protonation states of His88. This hydrogen-bond network is involved in monomer-monomer and dimer-dimer interactions, suggesting that the double protonation of His88 by acidification breaks the hydrogen-bond network and causes the destabilization of the TTR tetramer. Structural comparison with the X-ray crystal structure at acidic pH identified the three amino acid residues responsible for the pH sensitivity of TTR. Our neutron model provides insights into the molecular stability related to amyloidosis.
 -glucanase from Eisenia foetida
-glucanase from Eisenia foetidaArimori, Takao*; Ito, Akihiro*; Nakazawa, Masami*; Ueda, Mitsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro
no journal, ,
 - glucosyltransferase from
- glucosyltransferase from 
Hiromoto, Takeshi; Honjo, Eijiro*; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Ishiyama, Shintaro
no journal, ,
A prototype thermionic electron gun for a high-brightness X-ray generator has been developed. The X-ray generator is equipped with a newly designed rotating anticathode and aimed towards a maximum brilliance of 60 kWmm . During X-ray generation, the surface of the rotating anticathode has melt down spots due to the electron beam exposure, and these melting spots seems to induce damage of rotor and rotating balance. From view point of safety design toward structural soundness of this system, fluid and structural analysis to the rotor structure is absolutely imperative. In present study, dynamic fluid-structure interaction simulation techniques was applied to high-brightness X-ray generator and stress and deformation behavior during X-ray generation was analyzed.
. During X-ray generation, the surface of the rotating anticathode has melt down spots due to the electron beam exposure, and these melting spots seems to induce damage of rotor and rotating balance. From view point of safety design toward structural soundness of this system, fluid and structural analysis to the rotor structure is absolutely imperative. In present study, dynamic fluid-structure interaction simulation techniques was applied to high-brightness X-ray generator and stress and deformation behavior during X-ray generation was analyzed.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Kuroki, Ryota; Blaber, M.
no journal, ,
We have already succeeded in creation of the de novo designed protein (Symfoil) exhibiting the threefold symmetrical  -trefoil fold based on the human acidic fibroblast growth factor. Based on the Symfoil protein, we created Symfoil-II having the three repeats. The Symfoil-II protein was expressed in Eschericha coli as soluble protein, and purified by metal affinity chromatography using nickel-chelated agarose. The Symfoil-II was further purified by anion-exchange column chromatography after removing the HisTag by proteolysis. Symfoil-II was crystallized in 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH7.0) containing 1.8 M ammonium sulfate as precipitant at 20
-trefoil fold based on the human acidic fibroblast growth factor. Based on the Symfoil protein, we created Symfoil-II having the three repeats. The Symfoil-II protein was expressed in Eschericha coli as soluble protein, and purified by metal affinity chromatography using nickel-chelated agarose. The Symfoil-II was further purified by anion-exchange column chromatography after removing the HisTag by proteolysis. Symfoil-II was crystallized in 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH7.0) containing 1.8 M ammonium sulfate as precipitant at 20 C. The X-ray diffraction data was collected to 1.9
C. The X-ray diffraction data was collected to 1.9 resolution using a Rigaku R-AXIS VII diffractometer. The crystal belongs to a monoclinic space group C2. The refined crystal structure of Symfoil-II showed three fold symmetry as is observed in other Symfoils.
resolution using a Rigaku R-AXIS VII diffractometer. The crystal belongs to a monoclinic space group C2. The refined crystal structure of Symfoil-II showed three fold symmetry as is observed in other Symfoils.